1. Introduction
1.1 Importance of Vitamin D for Health
Vitamin D is often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin" because our bodies produce it when exposed to sunlight. This essential nutrient plays a vital role in maintaining overall health. It helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels, which are crucial for strong bones and teeth. Beyond bone health, Vitamin D also supports muscle function, boosts the immune system, and may even play a role in mood regulation.
When the body doesn't get enough Vitamin D, it can lead to a variety of health concerns. Understanding these issues begins with recognizing the Vitamin D deficiency symptoms that may arise.
1.2 Overview of Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms can manifest in many ways, ranging from subtle signs like fatigue and mood swings to more noticeable issues such as muscle weakness or frequent illnesses. These symptoms are often overlooked or mistaken for other conditions, making it critical to be aware of how deficiency presents itself.
Globally, Vitamin D deficiency is a widespread concern, affecting individuals across all age groups. Factors such as limited sun exposure, dietary restrictions, or certain medical conditions can increase the risk. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent long-term complications, including osteoporosis, cardiovascular issues, and weakened immunity.
This guide will explore the top 10 Vitamin D deficiency symptoms you should know, providing insight into their causes and what to watch for in your own health. By understanding these symptoms, you can take proactive steps to maintain optimal Vitamin D levels and improve your overall well-being.
Affiliate Disclaimer
This blog post may include links to affiliate sites. If you click on an affiliate link and make a purchase, we may earn a small commission or receive other compensation at no extra cost to you. Please note that many of the links on our site are affiliate links. Our use of these links does not impact the products, services, or websites we recommend to you. This disclaimer covers all forms of communication with you, including our website, email, phone, social media, products, and other platforms.
Amazon Affiliate Disclaimer
We participate in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate marketing program that allows us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and its affiliated sites. If you click on an Amazon affiliate link on our site and make a purchase, we may receive a small commission at no additional cost to you.
2. What Causes Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency is a common issue worldwide, affecting people across all age groups. Understanding the causes can help identify those at risk and take preventive steps. Below are the main factors contributing to this condition and how they can lead to Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
2.1 Lack of Sunlight Exposure
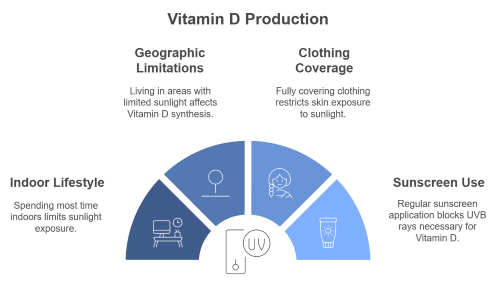
One of the primary sources of Vitamin D is sunlight. When UVB rays from the sun hit the skin, the body produces Vitamin D naturally. However, many people don’t get enough exposure due to:
- Spending most of their time indoors for work, school, or leisure
- Living in regions with limited sunlight, especially during winter months
- Wearing clothing that fully covers the skin, either for cultural or personal reasons
- Regular use of sunscreen, which blocks UVB rays
Without sufficient sunlight, the body's ability to produce Vitamin D drops significantly, leading to a range of Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms such as fatigue, weakened immunity, and bone pain.
2.2 Poor Dietary Intake
While sunlight is the main source, certain foods also provide Vitamin D. These include fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified products such as milk and cereals. Individuals who follow restrictive diets, such as veganism or those with food allergies, may miss out on these sources. This dietary gap can worsen Vitamin D deficiency, making it essential to monitor food choices to avoid Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
2.3 Medical Conditions and Medications
Certain medical conditions can interfere with Vitamin D absorption or metabolism, increasing the risk of deficiency. These include:
- Chronic kidney disease, which impairs the conversion of Vitamin D into its active form
- Digestive disorders like celiac disease or Crohn's disease, which hinder nutrient absorption
- Obesity, as excess body fat, can trap Vitamin D and make it less available for the body’s use
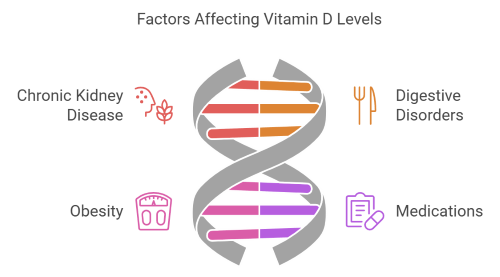
Medications like anticonvulsants, steroids, and weight-loss drugs can also interfere with Vitamin D levels, leading to symptoms such as muscle weakness and frequent illnesses.
2.4 Age and Skin Type
Age and skin type also play a role in Vitamin D deficiency. Older adults have a reduced ability to synthesize Vitamin D from sunlight, making them more prone to deficiency. Similarly, individuals with darker skin tones produce less Vitamin D due to higher melanin levels, increasing their risk of experiencing Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
2.5 Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Modern lifestyles contribute to deficiency as well. Urbanization has led to more time spent indoors, and air pollution can block UVB rays, reducing sun exposure. Additionally, the rise of sedentary behavior and limited outdoor activities exacerbate the problem.
By identifying these causes, individuals can take steps to minimize their risk and prevent Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms from impacting their health.
3. Top 10 Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms You Should Know
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, and its deficiency can lead to a wide range of symptoms. Recognizing these Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms early can help you take action to restore healthy levels and prevent long-term complications. Below are the top 10 symptoms to watch for, along with explanations of how they manifest.
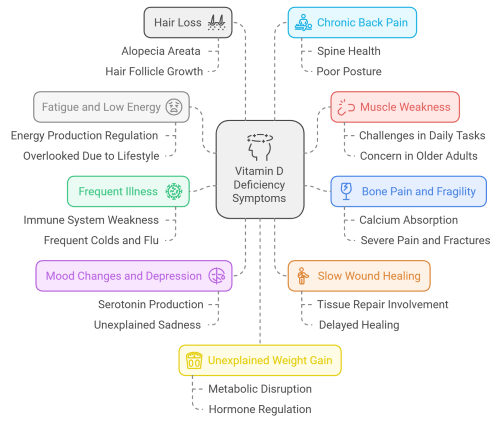
3.1 Fatigue and Low Energy
One of the earliest and most common Vitamin D deficiency symptoms is persistent fatigue. Vitamin D helps regulate energy production in the body, and a lack of it can leave you feeling tired even after adequate sleep. This symptom is often overlooked as it can easily be attributed to a busy lifestyle or stress.
3.2 Muscle Weakness
Vitamin D is vital for maintaining muscle strength. A deficiency can lead to feelings of weakness or heaviness in the muscles, making everyday tasks like climbing stairs or lifting objects more challenging. This symptom can affect individuals of all ages, though it is particularly concerning in older adults who are already at risk of falls.
3.3 Bone Pain and Fragility
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, a key mineral for bone health. Without enough Vitamin D, bones may become weak and brittle, leading to pain, discomfort, or even fractures. This is one of the more severe Vitamin D deficiency symptoms and often indicates long-term low levels of the vitamin.
3.4 Frequent Illness
A strong immune system relies on adequate Vitamin D levels. Deficiency can weaken your body’s ability to fight off infections, resulting in frequent colds, flu, or other illnesses. If you find yourself constantly falling sick, it may be worth checking your Vitamin D levels.
3.5 Mood Changes and Depression
Low levels of Vitamin D are linked to mood disorders, including depression. This is because Vitamin D influences the production of serotonin, a hormone that regulates mood. If you experience unexplained sadness or mood swings, it could be one of the lesser-known Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
3.6 Slow Wound Healing
Vitamin D is involved in tissue repair and inflammation control. A deficiency can delay the healing of cuts, scrapes, or surgical wounds. If you notice that wounds take unusually long to heal, it could be a sign of low Vitamin D levels.
3.7 Hair Loss
Severe Vitamin D deficiency can contribute to hair loss, especially in cases of alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition. This happens because Vitamin D plays a role in the growth of hair follicles. While not as common as other Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, it is still worth noting if hair loss is sudden or excessive.
3.8 Chronic Back Pain
Vitamin D supports the health of bones, including the spine. Deficiency can lead to persistent lower back pain that doesn’t improve with rest or pain relievers. This symptom is particularly common in individuals who sit for long periods or have poor posture.
3.9 Unexplained Weight Gain
Vitamin D influences metabolic processes and hormone regulation. Deficiency can disrupt these processes, potentially leading to weight gain that seems unrelated to diet or exercise changes. While this is not a definitive symptom, it may appear in conjunction with other Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
3.10 Cognitive Issues
Low Vitamin D levels are associated with brain fog, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems. This symptom may be subtle at first but can affect productivity and quality of life over time. For older adults, cognitive decline linked to Vitamin D deficiency is a significant concern.
By understanding these Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, you can monitor your health and seek medical advice if needed. Early detection is key to managing deficiency and restoring your well-being. If you notice any of these symptoms, consider checking your Vitamin D levels through a simple blood test and exploring ways to increase your intake.
4. How to Test for Vitamin D Deficiency
Testing for Vitamin D deficiency is a simple yet crucial step in understanding whether low levels of this vital nutrient are causing your symptoms. If you suspect Vitamin D deficiency symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, or frequent illness, testing can confirm your suspicions and guide the next steps for treatment.
4.1 Types of Vitamin D Tests
The most common way to determine your Vitamin D levels is through a blood test. This test measures the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in your blood, which is the best indicator of your Vitamin D status.
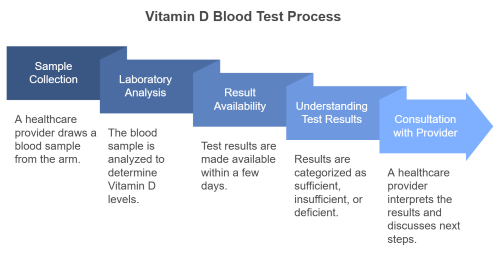
Blood Test Procedure
- A healthcare provider draws a small sample of blood from your arm.
- The sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Results are typically available within a few days.
The test results will show whether your Vitamin D levels are sufficient, insufficient, or deficient. Optimal levels typically range between 30 and 50 ng/mL, though this can vary slightly depending on the guidelines used.
4.2 When to Consider Testing
Testing for Vitamin D deficiency is particularly important if you are experiencing persistent Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms. These symptoms can range from chronic fatigue to more severe issues like bone pain and frequent infections. Testing is also recommended for individuals with higher risk factors, such as:
- Limited sun exposure due to geographic location or lifestyle
- Darker skin tones, as melanin reduces Vitamin D production
- Medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption, like celiac disease
- Older adults, who naturally produce less Vitamin D
If you belong to any of these groups or are experiencing unexplained health concerns, it’s wise to discuss testing with your healthcare provider.
4.3 Home Testing Kits
For convenience, home testing kits are also available. These kits typically involve pricking your finger to collect a small blood sample, which you then mail to a lab for analysis. While home tests can provide a general idea of your Vitamin D levels, they may not be as accurate as tests performed in a clinical setting.
4.4 Understanding the Results
Once you receive your test results, it’s important to interpret them with the help of a healthcare professional. Low levels may confirm the presence of Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, but a doctor can also help identify any underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments.
4.5 Follow-Up Testing
If you begin supplementation or other treatments to address deficiency, follow-up testing can help monitor your progress. This ensures your levels are improving and reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with Vitamin D deficiency.
By testing for Vitamin D deficiency, you gain valuable insight into your health and can take proactive steps to address any Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms you may be experiencing. Speak with your healthcare provider to determine if testing is right for you and start your journey toward better health today.
5. Treating and Preventing Vitamin D Deficiency
Addressing Vitamin D deficiency is essential to improve your overall health and manage Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms effectively. With the right strategies, you can restore optimal levels and prevent future deficiencies. Here are some effective ways to treat and prevent Vitamin D deficiency.

5.1 Increase Dietary Intake of Vitamin D
Diet plays a key role in maintaining healthy Vitamin D levels. While the list of Vitamin D-rich foods is limited, incorporating these into your meals can make a significant difference:
- Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods such as milk, orange juice, and cereals
- Cheese and certain types of mushrooms
For individuals experiencing Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, dietary changes alone may not suffice, but they can complement other treatment methods.
5.2 Spend More Time in the Sun
The most natural way to boost Vitamin D levels is through sunlight exposure. When UVB rays hit your skin, they stimulate the production of Vitamin D. To maximize this benefit:
- Aim for 10–30 minutes of sun exposure a few times a week, depending on your skin tone and location.
- Focus on exposing larger areas of skin, like arms and legs.
- Avoid peak sun hours to reduce the risk of sunburn.
Limited sun exposure is one of the primary reasons for Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, so making an effort to spend time outdoors can have significant benefits.
5.3 Vitamin D Supplements
For many individuals, especially those with moderate to severe deficiency, supplementation is the most effective way to restore Vitamin D levels. Options include:

- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol): The most commonly recommended supplement, as it is more effective at raising levels than Vitamin D2.
- Daily or weekly dosages, as prescribed by your healthcare provider, based on your blood test results.
Supplements are particularly beneficial for people who cannot rely on sunlight or dietary intake alone, such as those with certain medical conditions or who experience pronounced Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms.
5.4 Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
Once treatment begins, regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is crucial. Blood tests can track your progress and ensure you’re on the right dosage. Over-supplementation should be avoided, as excessively high Vitamin D levels can lead to toxicity.
5.5 Lifestyle Adjustments for Prevention
Preventing Vitamin D deficiency requires a proactive approach:
- Maintain a balanced diet that includes Vitamin D-rich foods.
- Prioritize outdoor activities to incorporate natural sunlight into your routine.
- Consider moderate supplementation during the winter months or if you live in areas with limited sunlight.
- Stay mindful of risk factors, such as certain medical conditions or lifestyle habits that may increase your susceptibility to deficiency.
5.6 Additional Considerations
For individuals with chronic health conditions or persistent Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms, it’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider. They can recommend tailored strategies to address the underlying causes and prevent recurrence.
By combining dietary changes, sunlight exposure, and supplementation, you can effectively treat Vitamin D deficiency and alleviate Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms. Prevention is equally important, as maintaining healthy levels is key to long-term well-being. Start taking steps today to prioritize your Vitamin D intake and protect your health.
6. Conclusion
6.1 Recap of Key Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms
Vitamin D deficiency can significantly impact your health, often presenting as subtle issues that are easy to overlook. Common Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, frequent illness, and mood changes. More severe symptoms like slow wound healing, hair loss, and cognitive difficulties may develop if the deficiency is prolonged. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being.
6.2 Importance of Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms Early
Proactively addressing Vitamin D deficiency is essential for your long-term health. Left untreated, low Vitamin D levels can lead to serious conditions such as osteoporosis, compromised immune function, and chronic pain. If you’re experiencing any symptoms, consult a healthcare provider to determine if Vitamin D deficiency is the root cause and discuss potential treatment options.
By increasing your dietary intake of Vitamin D, spending time outdoors, and considering supplementation, you can restore optimal levels and alleviate Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms. Regular testing and follow-up are important to ensure progress and prevent recurrence.
6.3 Final Thoughts
Maintaining adequate Vitamin D levels is a cornerstone of good health. Whether you’re taking steps to address current symptoms or aiming to prevent future deficiency, small changes in your lifestyle and diet can make a big difference. Take action today to prioritize your Vitamin D levels and enjoy the benefits of better energy, stronger immunity, and improved overall health.
FAQs
1. What are the most common Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms?
The most common symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, frequent illnesses, and mood changes such as depression. Some people may also experience hair loss, slow wound healing, or cognitive issues.
2. How is Vitamin D deficiency diagnosed?
A simple blood test measuring the levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) is used to diagnose Vitamin D deficiency. Optimal levels typically range between 30 and 50 ng/mL.
3. Who is most at risk for Vitamin D deficiency?
Those at higher risk include people with limited sun exposure, darker skin tones, older adults, individuals with certain medical conditions (like celiac or Crohn’s disease), and those following restrictive diets.
4. Can Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms improve with sunlight exposure?
Yes, spending time in sunlight helps the body produce Vitamin D, which can alleviate symptoms over time. Aim for 10–30 minutes of sun exposure several times a week, depending on your skin tone and location.
5. What foods are rich in Vitamin D?
Foods rich in Vitamin D include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), egg yolks, fortified milk or cereals, and mushrooms exposed to UV light.
6. How long does it take to recover from Vitamin D deficiency?
Recovery time varies based on the severity of the deficiency and the treatment plan. With proper supplementation and lifestyle changes, noticeable improvement in symptoms can occur within a few weeks to months.
7. Can you take too much Vitamin D?
Yes, excessive Vitamin D supplementation can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, kidney damage, or calcium buildup in the blood. Always follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for dosage.


